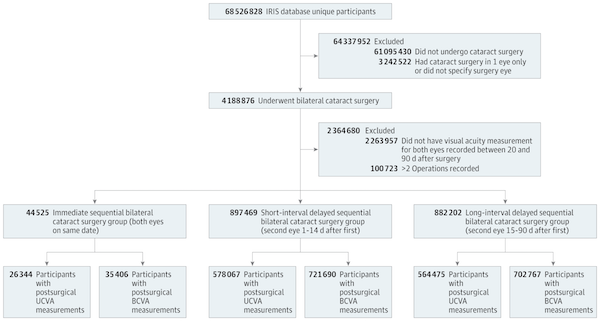
In this large population-based study using data from American Academy of Ophthalmology Intelligent Research in Sight (IRIS) Registry, Dr. Cecilia Lee and her co-authors looked at visual acuity outcomes after bilateral cataract surgery. Specifically, they compared outcomes after immediate sequential bilateral cataract surgery or ISBCS (patients undergo surgery for both eyes on the same day, as separate procedures), and delayed sequential cataract surgery or DSBCS (patients have the surgeries on separate days). ISBCS is less commonly performed in the United States, but is growing in popularity and may have some advantages such as fewer follow-up visits, immediate vision correction, and lower cost. However, many ophthalmologists prefer delaying the second surgery in order to assess vision after the first surgery, in order to make adjustments for the second eye.
Continue reading "Refractive Outcomes After Immediate Sequential vs Delayed Sequential Bilateral Cataract Surgery"Application of deep learning to understand resilience to Alzheimer's disease pathology
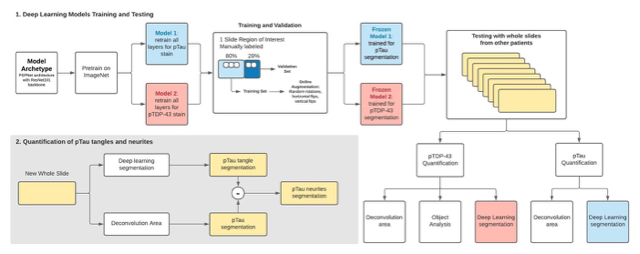
The term "resilient" is used to describe the unique set of people who develop the neuropathological features of Alzheimer's disease but do not show signs of the cognitive decline that is typically associated with the disease. In this study, published in the journal Brain Pathology, Dr. Cecilia Lee and Dr. Aaron Lee used a machine learning approach to identify subtle differences in brain tissue of "resilient" patients compared to patients with Alzheimer's disease. These patients had been participants in the Adult Changes in Thought study and donated their brains for research into the causes of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias.
Continue reading "Application of deep learning to understand resilience to Alzheimer's disease pathology"Recommendations for Standardization of Images in Ophthalmology
In this editorial, writing for the American Academy of Ophthalmology, Dr. Aaron Lee and his co-authors explain the urgent need for ophthalmic imaging device manufacturers to standardize their imaging formats to comply with existing international standards. Currently, manufacturers of devices such as optical coherence tomography machines use their own proprietary imaging formats, requiring special software to access and analyze the images obtained with their device. This common practice makes it difficult for clinicians and researchers to compare images from different machines. Standardization would allow interoperability between imaging systems, allowing electronic health information to be transferred more easily when a patient is seen at different hospitals or clinics. It would also allow researchers to build comprehensive imaged datasets for and big data analyses and machine learning studies, a growing area of research in ophthalmology that is currently limited by lack of image standardization.
Continue reading "Recommendations for Standardization of Images in Ophthalmology"Associations Between Retinal Artery/Vein Occlusions and Risk of Vascular Dementia
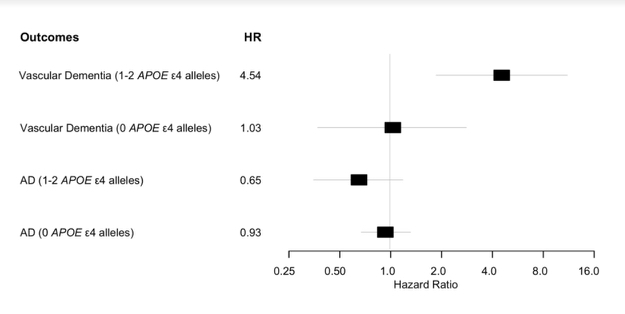
In this study published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, Dr. Cecilia Lee and her co-authors investigated whether retinal artery and retinal vein occlusions are risk factors for developing dementia. Retinal vascular occlusions are associated with aging and can reflect systemic vascular changes related to diseases like hypertension and cardiovascular disease, changes that may also be occurring in the brain. Vascular pathology is already known to be an important risk factor for Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Dr. Lee wondered if retinal vascular occlusion might be a harbinger for problems with cognition down the line.
Continue reading "Associations Between Retinal Artery/Vein Occlusions and Risk of Vascular Dementia"Understanding the Brain through Aging Eyes
In this Viewpoint article published in the journal Advances in Geriatric Medicine and Research, Dr. Cecilia Lee discusses the ways in which the eye, specifically the retina, can provide valuable information about the aging brain and dementia. The eye and the brain share the same embryologic origins and undergo similar changes as we age. One reason that it is challenging to develop treatments for neurodegenerative diseases associated with aging such as Alzheimer's disease is that it is very difficult to examine brain tissue while a person is living. The retina, however, can be visualized easily and non-invasively in an ophthalmology clinic or doctor's office, and can provide interesting clues about disease processes in the brain.
Continue reading "Understanding the Brain through Aging Eyes"