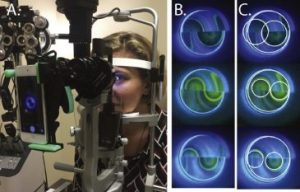
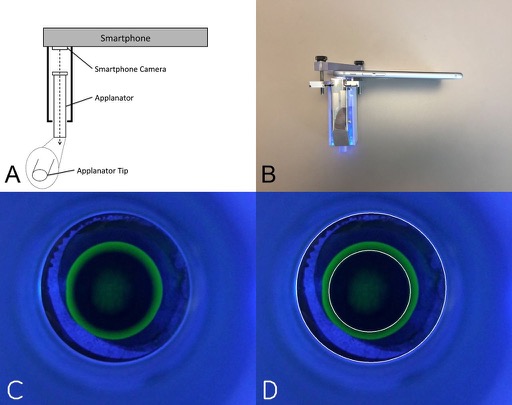
This study describes a novel method for automating Goldman Applanation Tonometry (GAT) measurements using a deep learning approach. GAT is the gold standard method for measuring intraocular pressure, which is an essential metric in the management of glaucoma.
To obtain accurate intraocular pressure measurements using traditional GAT, the user must use a dial to adjust the device to align two visible circular "mires", in order to determine the correct amount of force needed to create a fixed area of applanation on the surface of the eye, which is then used to calculate the intraocular pressure. This somewhat subjective alignment procedure can produce different results between users, and studies have found other unintended biases such as a preference for even-numbered readings on the dial. The goal of this study was to provide a method for obtaining more objective and reproducible GAT readings, by training a deep learning based algorithm to accurately recognize and measure the mires produced from a fixed application of force, and then use the measurements to calculate the intraocular pressure.
Continue reading "Using Deep Learning to Automate Goldmann Applanation Tonometry Readings"