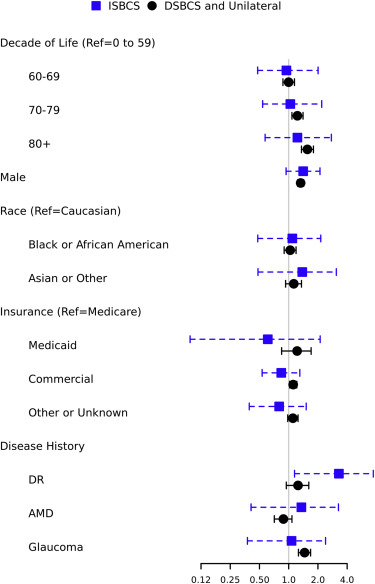
This large retrospective cohort study used data from more than 5 million people who underwent bilateral cataract surgery in the United States to investigate the rate of post-operative endophthalmitis. The authors compared the rates of endophthalmitis in the group of patients who had both eye surgeries on the same day (immediate sequential bilateral cataract surgery, or ISBCS) to the group of patients who either had cataract surgery in both eyes on separate days (delayed sequential bilateral cataract surgery) or who just had surgery in one eye. The authors found that after controlling for age, sex, race, insurance status, and comorbid eye diseases, the risk of postoperative endophthalmitis was not statistically significantly different between these two groups, .
Continue reading "Endophthalmitis Rate in Immediately Sequential versus Delayed Sequential Bilateral Cataract Surgery within the Intelligent Research in Sight (IRIS) Registry Data"Identification of torque teno virus in culture-negative endophthalmitis by representational deep DNA sequencing.
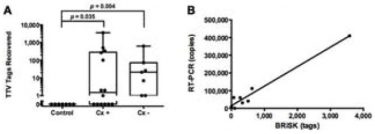
Although rare, infectious endophthalmitis is among the most serious post-surgical complications of ophthalmic surgery because it can result in serious vision loss. The standard technique for diagnosing endophthalmitis is microbial culture, but this technique fails to identify an organism in many cases. 16S polymerase chain reaction is more sensitive and specific than traditional culture techniques, but is limited to bacteria and cannot detect fungi (which require separate fungal rDNA ribosomal PCR), parasites, or viruses. Biome Representational in Silico Karyotyping (BRiSK) is a newer technique used to purify a defined fraction of all DNA present in a sample and sequence it to near saturation, allowing for the identification of most known bacteria, as well as phage, viruses, and previously unknown organisms. In this study, the authors applied this deep DNA sequencing technique to vitreous and aqueous biopsies from patients with endophthalmitis to test the hypothesis that uncultured organisms may be present in cases of culture-negative endophthalmitis.
Continue reading "Identification of torque teno virus in culture-negative endophthalmitis by representational deep DNA sequencing."