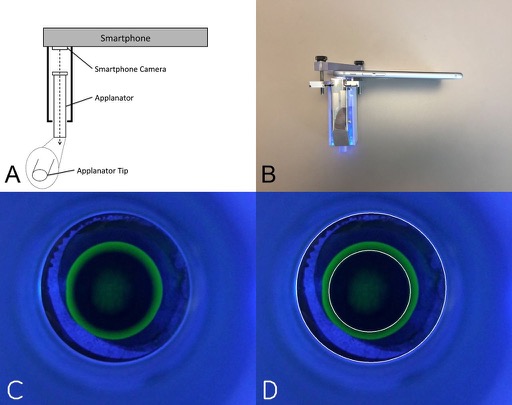
Access to eye care in more rural and remote areas can be challenging, because ophthalmologists need certain types of examination equipment that can be large and difficult to transport. Advances in smartphone technology are helping to address this problem - better cameras, software, and hardware attachments have the potential to allow ophthalmologists to bring a portable examining room to previously underserved areas.
Continue reading "Development and validation of a machine learning, smartphone-based tonometer"To Err is Both Human and AI
In a recent Outlook commentary in the journal Nature, Dr. Aaron Lee discusses the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in clinical medicine - both the significant potential for this technology as well as the various limitations and ethical issues involved with its implementation. He specifically addresses the case of AI screening systems for diabetic retinopathy - the first of these has already been approved for use by the FDA - but the issues with these systems apply to other areas of clinical medicine beyond ophthalmology. Dr. Lee makes the case that as this technology improves, and especially with the potential for deep learning algorithms to "learn" from their mistakes, the benefits from using AI as a tool for physicians may outweigh the risks.
Continue reading "To Err is Both Human and AI"Fully automated, deep learning segmentation of oxygen-induced retinopathy images
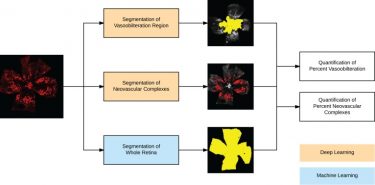
In this paper, published in JCI Insight, the authors describe their deep learning model for quantifying vaso-obliteration and neovascularization on retinal images, which are key measurements in oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model studies of ischemia-driven neovascularization. The mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy is one of the most commonly used in vivo models to study basic mechanisms in ocular angiogenesis and to test potential therapeutics. Measurements of vaso-obliteration and neovascularization are often used in proof-of-concept studies evaluating antiangiogenic drugs for diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy.
Continue reading "Fully automated, deep learning segmentation of oxygen-induced retinopathy images"