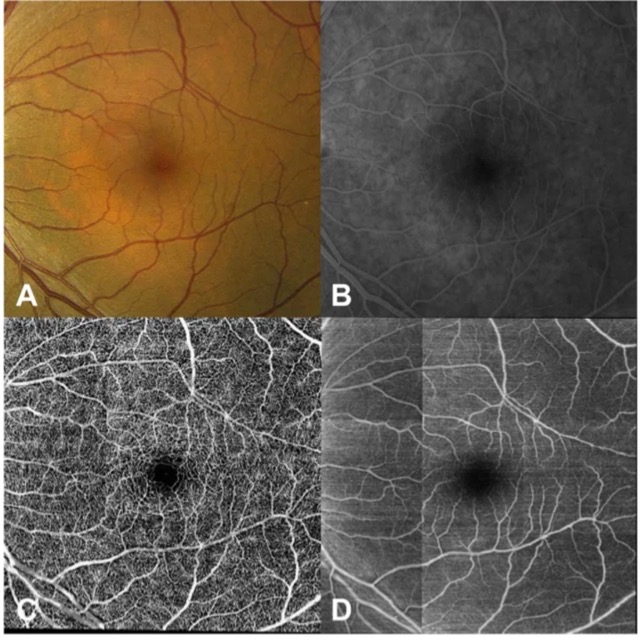
Advances in both imaging technology and artificial intelligence are enabling many new developments in the field of ophthalmology. Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) is one such development. OCTA measures blood flow in retinal microvasculature and can visualize the superficial and deep capillary plexus of the retinal vasculature without the need for dye. But the technology is also expensive and has a limited field of view. In this study, we sought to develop a deep learning model that could address this issue by first learning to infer between structure and retinal vascular function from structural OCT images and then generating an OCTA-like image. This would allow for accurate objectively-generated annotations, eliminating the need for expert-defined labels, and potentially enable the acquisition of new information about retinal blood circulation from preexisting OCT databases.
Taking advantage of an already existing imaging modality as the ground truth, our model generated detailed flow maps of the retinal vessels in a variety of retinal conditions. The model successfully identified both the retinal vessels that were easily seen on structural OCT B-scan images as well as the retinal microvasculature that was not apparent to the clinician on standard OCT, and showed significantly more retinal vessels compared to structural OCT en-face projections, color and FA images.
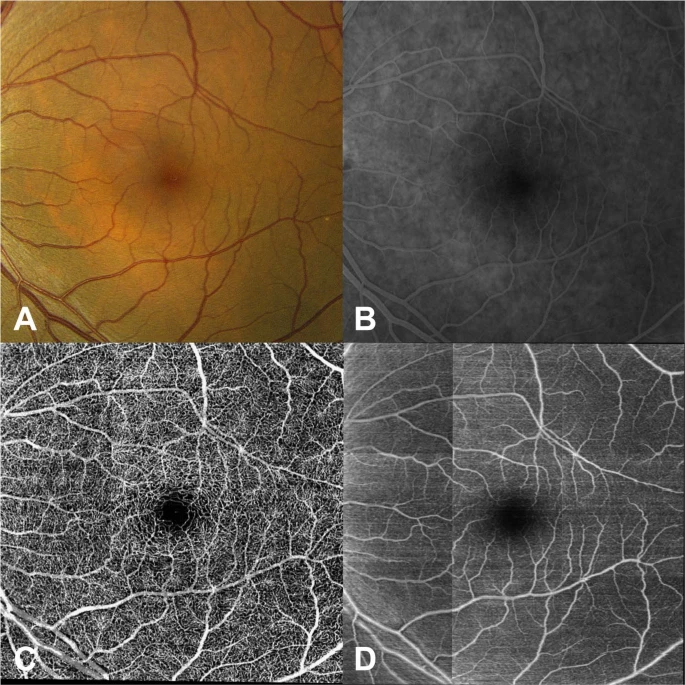
Our study demonstrates that a deep learning model can be trained to recognize features of OCT images that allow successful identification of retinal vasculature on cross sectional OCT scans in a fully automated fashion and generate projection flow maps. Unlike current AI models which are primarily targeted towards classification or segmentation of images, to our knowledge, this is the first application of artificial neural networks in ophthalmic imaging to generate a new image based on data from a different imaging modality.
Lee CS, Tyring AJ, Wu Y, Xiao S, Rokem AS, DeRuyter NP, Zhang Q, Tufail A, Wang RK, Lee AY. Generating retinal flow maps from structural optical coherence tomography with artificial intelligence. Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 5;9(1):5694. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019- 42042-y. PubMed PMID: 30952891; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6450899.