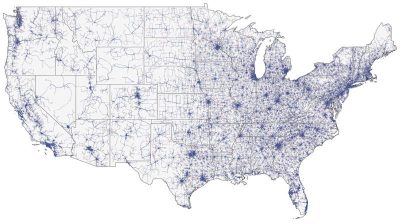
In this important study, Dr. Cecilia Lee, Dr. Aaron Lee, and their co-authors used census and mapping data to quantify how far Medicare patients travel to access eye care in the contiguous United States. This type of information about medically underserved geographic areas is essential for improving access to care. The authors note that the issue of rural access to care has been cited as a reason for increasing the number of eye care providers in the United States. Some providers also use access to care as an argument for increasing optometrists' responsibilities and scope of practice.
Continue reading "Evaluating Access to Eye Care in the Contiguous United States by Calculated Driving Time in the United States Medicare Population"Patterns of Laboratory Testing Utilization Among Uveitis Specialists
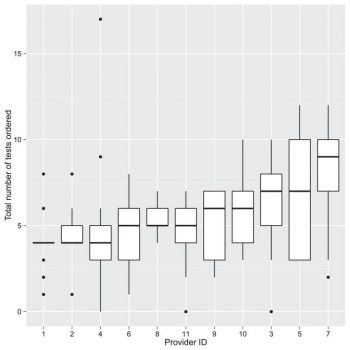
The purpose of this interesting study by Dr. Lee and her co-authors was to better understand how ophthalmologists order tests when evaluating patients with uveitis. There are about 150,000 cases of uveitis (inflammation of the uvea) in the United States each year, and testing for treatable diseases as well as other health issues that might be associated with uveitis is an important part of the workup when patients present with this condition. However, unlike many other ophthalmic conditions, there is no "standard laboratory workup" for uveitis, and unfocused ordering of diagnostic tests can be difficult to interpret and costly.
Continue reading "Patterns of Laboratory Testing Utilization Among Uveitis Specialists"Scalable metagenomics alignment research tool (SMART): a scalable, rapid, and complete search heuristic for the classification of metagenomic sequences from complex sequence populations
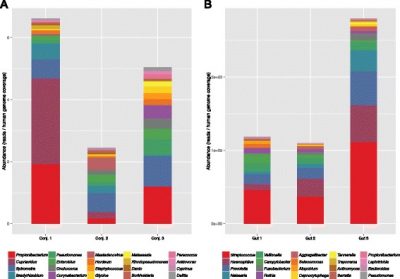
In this study, the authors address a relatively new computational challenge: how to to rapidly and accurately identify species-level DNA sequences from next generation metagenomic shotgun sequencing data. NCBI Genbank (v209), the ever-growing library of sequenced DNA fragments mapped to an identified taxonomy species, has an enormous catalog (1.99 x 1011 basepairs of cDNA and genomic DNA from 1.87 x 108 records at the time of this study). Sequence alignment software is used to match unknown DNA sequences to the catalog of identified genetic data, but new approaches are needed to manage the increasing data. In this study, the authors aimed to validate a Scalable Metagenomics Alignment Research Tool (SMART), a novel searching heuristic for shotgun metagenomics sequencing results.
Continue reading "Scalable metagenomics alignment research tool (SMART): a scalable, rapid, and complete search heuristic for the classification of metagenomic sequences from complex sequence populations"Previous Intravitreal Therapy Is Associated with Increased Risk of Posterior Capsule Rupture during Cataract Surgery
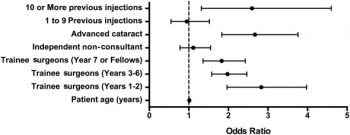
In this multicenter, national electronic medical record database study, Dr. Lee and his coauthors investigated whether previous intravitreal therapy is a predictor of posterior capsule rupture during cataract surgery. Posterior capsule rupture occurs in approximately 1.9% to 2.1% of cataract surgeries and is the only potentially modifiable risk indicator for visual loss after cataract surgery. There are many known risk factors for posterior capsule rupture, but the significance of previous intravitreal therapy, an increasingly common treatment for several ophthalmic conditions, as a risk factor for this complication of cataract surgery is unknown.
Continue reading "Previous Intravitreal Therapy Is Associated with Increased Risk of Posterior Capsule Rupture during Cataract Surgery"Use of Mechanical Turk as a MapReduce Framework for Macular OCT Segmentation
In this study published in the Journal of Ophthalmology, the authors experimented with distributing the work of performing a large complex image labeling task (identifying layers of the retina on multiple optical coherence tomography images) using a popular crowdsourcing marketplace. Optical coherence tomography is an important noninvasive diagnostic tool in the field of ophthalmology, especially for the management of age-related macular degeneration, a common cause of blindness in the developed world. However, the automated measurements provided by the optical coherence tomography software result in frequent errors for critical parameters such as macular thickness and volume. Human eyes have the ability to identify and complete areas on the image where there is poor signal to noise ratio and are better at recognizing complex pathology. The authors sought to evaluate the feasibility of using Mechanical Turk as a parallel platform to allow multiple people to simultaneously and rapidly perform manual segmentations (identification of retinal layer boundaries) of the images.
Continue reading "Use of Mechanical Turk as a MapReduce Framework for Macular OCT Segmentation"