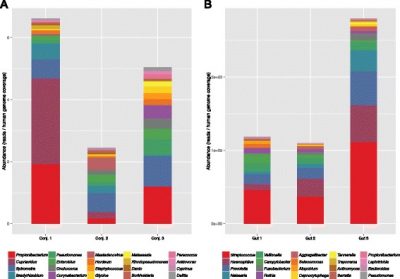
In this study, the authors address a relatively new computational challenge: how to to rapidly and accurately identify species-level DNA sequences from next generation metagenomic shotgun sequencing data. NCBI Genbank (v209), the ever-growing library of sequenced DNA fragments mapped to an identified taxonomy species, has an enormous catalog (1.99 x 1011 basepairs of cDNA and genomic DNA from 1.87 x 108 records at the time of this study). Sequence alignment software is used to match unknown DNA sequences to the catalog of identified genetic data, but new approaches are needed to manage the increasing data. In this study, the authors aimed to validate a Scalable Metagenomics Alignment Research Tool (SMART), a novel searching heuristic for shotgun metagenomics sequencing results.
Continue reading "Scalable metagenomics alignment research tool (SMART): a scalable, rapid, and complete search heuristic for the classification of metagenomic sequences from complex sequence populations"Previous Intravitreal Therapy Is Associated with Increased Risk of Posterior Capsule Rupture during Cataract Surgery
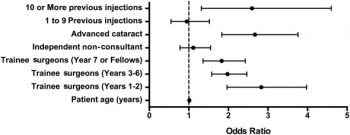
In this multicenter, national electronic medical record database study, Dr. Lee and his coauthors investigated whether previous intravitreal therapy is a predictor of posterior capsule rupture during cataract surgery. Posterior capsule rupture occurs in approximately 1.9% to 2.1% of cataract surgeries and is the only potentially modifiable risk indicator for visual loss after cataract surgery. There are many known risk factors for posterior capsule rupture, but the significance of previous intravitreal therapy, an increasingly common treatment for several ophthalmic conditions, as a risk factor for this complication of cataract surgery is unknown.
Continue reading "Previous Intravitreal Therapy Is Associated with Increased Risk of Posterior Capsule Rupture during Cataract Surgery"UK AMD EMR USERS GROUP REPORT V: benefits of initiating ranibizumab therapy for neovascular AMD in eyes with vision better than 6/12
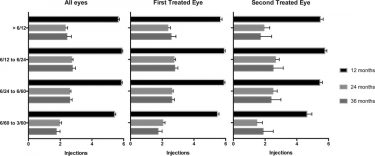
Neovascular age-related macular degeneration is characterized by the growth of abnormal, choroidal blood vessels beneath the macula. When left untreated, these blood vessels can lead to severe loss of vision. Intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor-A drugs is an established therapy that helps to prevent the growth of these abnormal vessels. In the United Kingdom, this treatment is provided for patients with visual acuity in the range of 6/12-6/96, consistent with the pivotal trials that were conducted to approve the use of this therapy. As the use of intravitreal therapy for age-related macular degeneration has increased, studies have suggested that starting treatment earlier in the disease process, before patients have significant vision loss, can help to preserve vision longer. In this study, the authors used data from thousands of patients from multiple health centers in the United Kingdom to further evaluate this effect on a large scale.
Continue reading "UK AMD EMR USERS GROUP REPORT V: benefits of initiating ranibizumab therapy for neovascular AMD in eyes with vision better than 6/12"