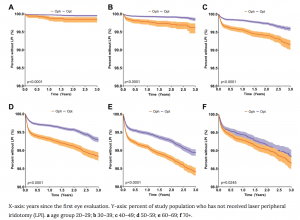
In this large retrospective study published in the journal Eye, Dr. Cecilia Lee and her co-authors reviewed data from a Massachusetts claims database to assess how certain risk factors for glaucoma are detected and diagnosed during an eye exam. The authors compared outcomes from both ophthalmologists and optometrists to determine if there were any differences in how often they referred at-risk patients for further evaluation and treatment.
Primary angle closure glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide, affecting ~26% of the glaucoma population globally. Timely detection of occludable narrow angles (condition that can sometimes progress to primary angle closure glaucoma) in patients who are at risk is a key method of prevention. If indicated, patients can be referred for laser peripheral iridotomy to prevent more serious outcomes.
Continue reading "Predictors of Narrow Angle Detection Rate-A Longitudinal Study of Massachusetts Residents Over 1.7 Million Person Years"