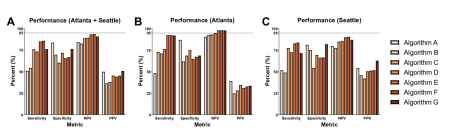
In this article published in the journal Diabetes Care, Dr. Aaron Lee and his co-authors put diabetic retinopathy screening algorithms to the test in the real world, evaluating them on retinal images from nearly 24,000 veterans who sought diabetic retinopathy screening at two Veterans Affairs health care systems (Seattle and Atlanta). These screening algorithms are designed to check patients who might be at risk for retinopathy, a potential complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness if left untreated. Based on performance in clinical trials, one of these algorithms is approved for use in the US, and several others are in clinical use in other countries. Dr. Lee wanted to know how well they worked outside of the clinical trial setting, however, when faced with real world data from a diverse group of patients in a variety of clinical settings.
Continue reading "Multicenter, Head-to-Head, Real-World Validation Study of Seven Automated Artificial Intelligence Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Systems"Ophthalmology-Based Neuropathology Risk Factors: Diabetic Retinopathy is Associated with Deep Microinfarcts in a Community-Based Autopsy Study.
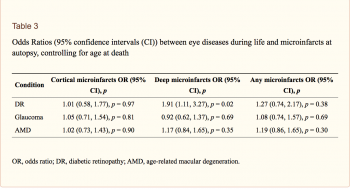
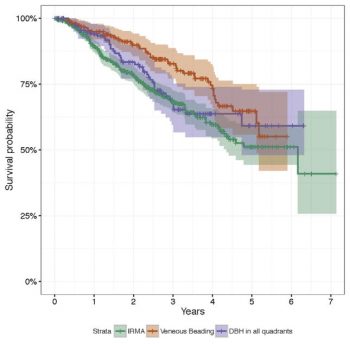
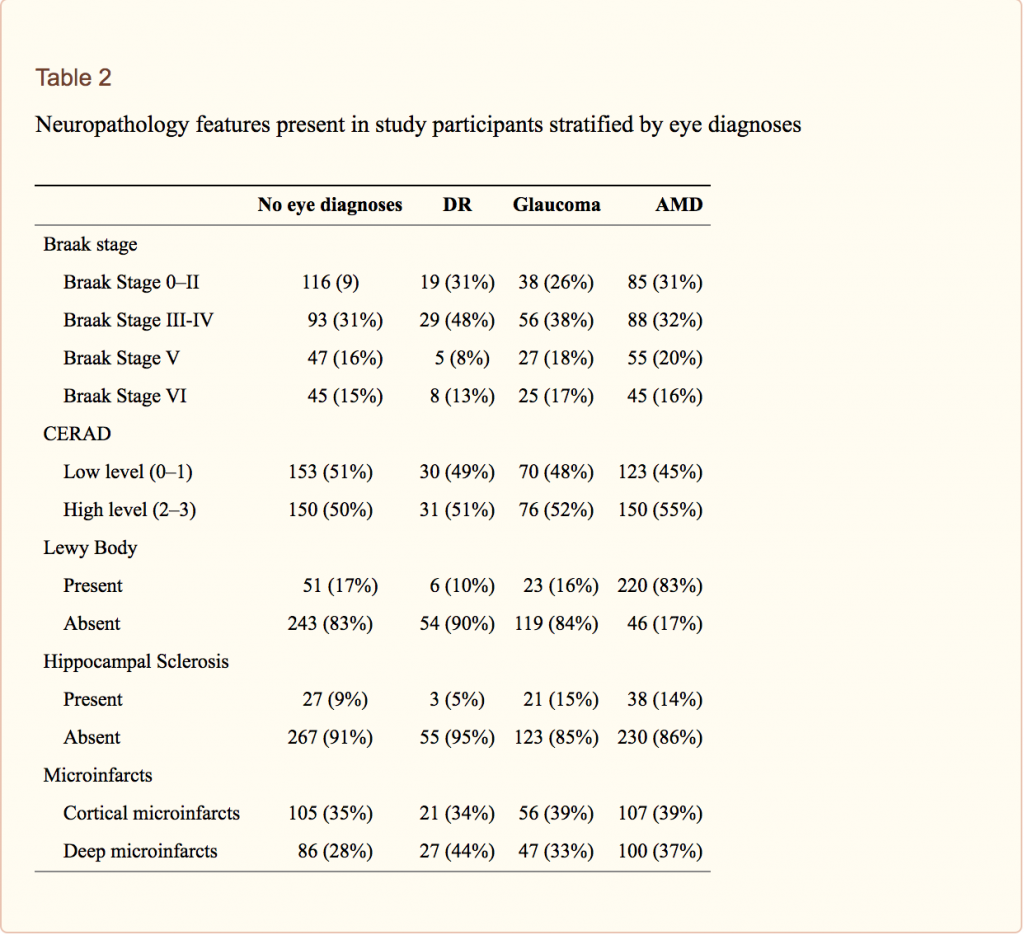
The eye offers opportunities to capture critical information regarding the health of the brain, as the neurological anatomy and the microvasculature of the retina are very closely related to those of the brain and can be similarly affected by certain pathological processes. In this study published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, Dr. Cecilia Lee and her co-authors compared brain neuropathology findings with known clinical information to determine if there were any associations between certain eye diseases and the presence of characteristic neuropathologic lesions of Alzheimer's disease. The authors analyzed the data from 676 patients from Adult Changes in Thought, a prospective longitudinal study in older patients who are followed over time and monitored for development of cognitive decline and dementia.
Associations between recent and established ophthalmic conditions and risk of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease affects millions of adults and is the most common type of dementia. Identifying risk factors for Alzheimer's may lead to early detection and preventive measures that are based on a better understanding of the disease processes involved. The eye provides substantial information on brain health, and may give some clues to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Eye conditions such as glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy have some shared characteristics with Alzheimer's disease, such as progressive neurodegeneration, characteristic amyloid beta deposits, and microvascular disease. This study aimed to investigate potential associations between four eye conditions (glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and cataract) with Alzheimer's disease in a large cohort of patients.
Continue reading "Associations between recent and established ophthalmic conditions and risk of Alzheimer's disease"The United Kingdom Diabetic Retinopathy Electronic Medical Record Users Group: Report 3: Baseline Retinopathy and Clinical Features Predict Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy
In this large study using data from more than 30,000 patients in the UK, the authors analyzed potential risk factors for developing proliferative diabetic retinopathy and vitreous hemorrhage in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic retinopathy is a major cause of blindness in working-age adults, and early detection can substantially decrease the risk of progression to vision loss. Patients with diabetes should have regular screening for early signs of diabetic retinopathy, but the current severity classification systems may not be the most accurate method for predicting which patients are most at risk for vision-threatening disease, particularly as standards of care have been updated.
Continue reading "The United Kingdom Diabetic Retinopathy Electronic Medical Record Users Group: Report 3: Baseline Retinopathy and Clinical Features Predict Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy"