In this study, the authors created and tested an algorithm for extracting visual acuity testing information from clinical notes. The increasing use of electronic health records is allowing for large-scale data review in clinical research. The data accessed from electronic health records can be limited, however, because the manually transcribed data is often stored as free text. Automated conversion of free text into machine-readable data and extraction for research requires the application of computational linguistics and natural language processing.
In ophthalmology, visual acuity is an important outcome measure used throughout vision research. Documentation of visual acuity in the clinical record is often in the form of free text, requiring interpretation if the data are to be extracted. To make this data more accessible, the authors developed the total visual acuity extraction algorithm (TOVA) to extract best-corrected visual acuity data from free text ophthalmology consultation notes. The algorithm applies natural language processing to recognize Snellen visual acuity in free text notes and assign laterality. The best corrected measurement is determined for each eye and then converted to logMAR.
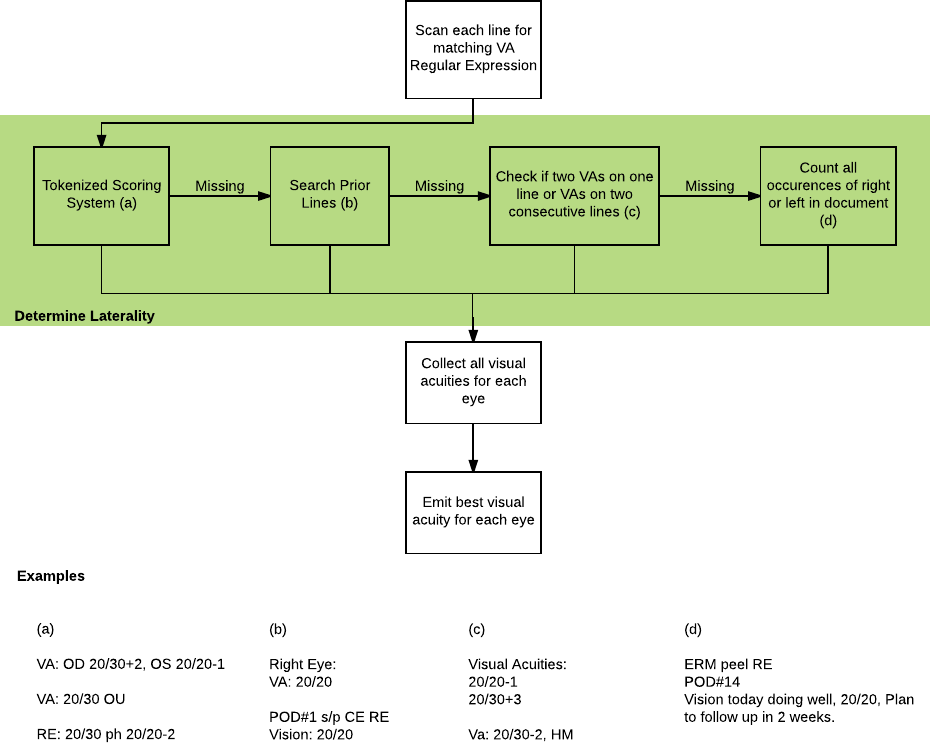
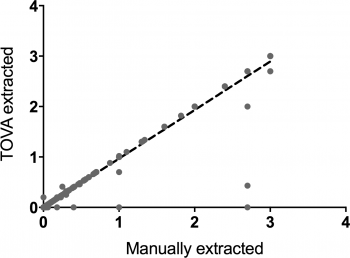
To test the algorithm, the authors compared its results to manually extracted data from of a subset of the notes. The algorithm was quite accurate, showing 95% agreement with the manually extracted data. In addition, it worked quickly, processing 6266 patient notes in less than a second. One of the unique strengths of the algorithm is that it is capable of assigning laterality from free text using a tokenized scoring system.
This study demonstrates that a natural language processing approach works well for visual acuity data and has the potential to provide fast, accurate, large-scale data extraction from EHRs allowing more possibilities for future clinical studies.
Baughman DM, Su GL, Tsui I, Lee CS, Lee AY. Validation of the Total Visual Acuity Extraction Algorithm (TOVA) for Automated Extraction of Visual Acuity Data From Free Text, Unstructured Clinical Records. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2017 Mar;6(2):2. doi: 10.1167/tvst.6.2.2. eCollection 2017 Mar. PubMed PMID: 28299240; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5347661.