In this study, the authors developed a convolutional neural network that successfully detected intraretinal fluid on ocular coherence tomography images. Macular edema, characterized by loss of the blood retinal barrier in very small retinal blood vessels, leads to the accumulation of fluid in the retina that can interfere with vision. The degree of macula edema present is usually inferred by measuring central retinal thickness on ocular coherence tomography images, but this measurement does not fully capture the extent and severity of the intraretinal fluid present.
Continue reading "Deep-learning based, automated segmentation of macular edema in optical coherence tomography"The United Kingdom Diabetic Retinopathy Electronic Medical Record Users Group: Report 3: Baseline Retinopathy and Clinical Features Predict Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy
In this large study using data from more than 30,000 patients in the UK, the authors analyzed potential risk factors for developing proliferative diabetic retinopathy and vitreous hemorrhage in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic retinopathy is a major cause of blindness in working-age adults, and early detection can substantially decrease the risk of progression to vision loss. Patients with diabetes should have regular screening for early signs of diabetic retinopathy, but the current severity classification systems may not be the most accurate method for predicting which patients are most at risk for vision-threatening disease, particularly as standards of care have been updated.
Continue reading "The United Kingdom Diabetic Retinopathy Electronic Medical Record Users Group: Report 3: Baseline Retinopathy and Clinical Features Predict Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy"UK AMD/DR EMR REPORT IX: comparative effectiveness of predominantly as needed (PRN) ranibizumab versus continuous aflibercept in UK clinical practice
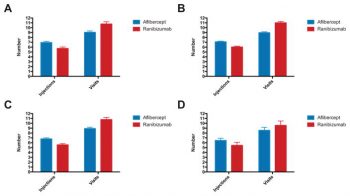
In this multicenter study in the UK, the authors analyzed the electronic medical records of patients with age-related macular degeneration and compared two different drugs, ranibizumab and aflibercept, commonly used to treat this disease. Neovascular age-related macular degeneration is characterized by choroidal neovascularisation, which is responsible for the majority of visual loss. Intravitreal injections with vascular endothelial growth factor-A inhibitor drugs can reduce abnormal blood vessel growth and improve vision. This studied compared the effectiveness of two of these drugs, ranibizumab and aflibercept, by analyzing the visual acuity outcomes in patients who received either drug over a one year period.
Continue reading "UK AMD/DR EMR REPORT IX: comparative effectiveness of predominantly as needed (PRN) ranibizumab versus continuous aflibercept in UK clinical practice"Validation of the Total Visual Acuity Extraction Algorithm (TOVA) for Automated Extraction of Visual Acuity Data From Free Text, Unstructured Clinical Records
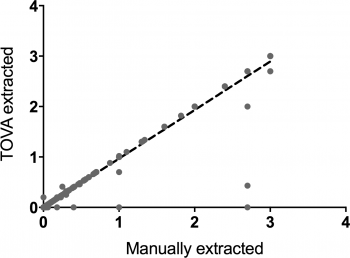
In this study, the authors created and tested an algorithm for extracting visual acuity testing information from clinical notes. The increasing use of electronic health records is allowing for large-scale data review in clinical research. The data accessed from electronic health records can be limited, however, because the manually transcribed data is often stored as free text. Automated conversion of free text into machine-readable data and extraction for research requires the application of computational linguistics and natural language processing.
Continue reading "Validation of the Total Visual Acuity Extraction Algorithm (TOVA) for Automated Extraction of Visual Acuity Data From Free Text, Unstructured Clinical Records"Deep learning is effective for the classification of OCT images of normal versus Age-related Macular Degeneration
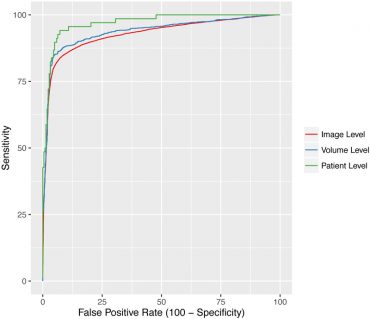
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is the most commonly obtained imaging modality in ophthalmology and represents a dense and rich imaging dataset when combined with labels derived from the electronic medical record. In this study, the authors developed a novel deep learning approach to distinguish normal OCT images from images from patients with age-related macular degeneration.
Continue reading "Deep learning is effective for the classification of OCT images of normal versus Age-related Macular Degeneration"